Neurofeedback & Brain Recovery
7138999589 • May 28, 2025
Neurofee dback & Brain Recovery

Neurofeedback therapy, also known as EEG biofeedback, is a non-invasive brain training method that helps individuals regulate their brain activity. By using real-time feedback from brainwave monitoring (typically through QEEG or EEG), patients learn to optimize neural patterns that may be associated with dysfunction, such as anxiety, attention problems, or cognitive deficits.
🔬 What Happens During Neurofeedback Therapy?
Brainwave Recording: Sensors are placed on the scalp to monitor brain activity.
Real-Time Feedback: The system provides visual, auditory, or tactile feedback (e.g., a movie playing only when the brain is in a desired state).
Learning and Reinforcement: Over time, the brain learns to self-regulate—reducing undesirable patterns and increasing optimal ones.
🧠 Why Neurofeedback Matters for Brain Recovery
Neurofeedback is especially important for brain recovery after injury or in neurological dysfunction for several reasons:
1. Restores Functional Connectivity
After concussion, stroke, or trauma, the brain’s networks often become dysregulated.
Neurofeedback helps restore neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to rewire and heal.
2. Targets Specific Dysfunctions
Different brain regions are responsible for mood, focus, memory, and motor control.
Neurofeedback customizes training to target dysregulated areas (e.g., alpha uptraining for calming the brain, SMR for focus and sleep).
3. Reduces Symptoms Without Medication
Shown to help with:
Anxiety, depression, PTSD
ADHD and cognitive dysfunction
Post-concussion syndrome
Chronic pain and insomnia
4. Promotes Autonomy
Unlike medication or passive treatments, neurofeedback teaches the brain to self-correct.
Improvements often remain even after sessions end because the brain has "learned" better functioning.
🧪 What Does the Research Say?
ADHD: Meta-analyses show improvements in attention and impulse control (Arns et al., 2009).
TBI: Improved cognitive flexibility and reduced post-concussive symptoms (Duff et al., 2004).
Anxiety/Depression: Normalizes over-activation in limbic areas (Hammond, 2005).
📈 Summary
Benefit How Neurofeedback Helps
Brain injury recovery Enhances neuroplasticity and reorganization
Emotional regulation Trains limbic and prefrontal regions
Attention/focus Improves executive function and frontal lobe control
Sleep & energy Balances slow-wave vs fast-wave brain activity
Learn more about Neurofeedback therapy at Synapse Brain & Spine Center located in Lewes Delaware by calling 302-200-7965
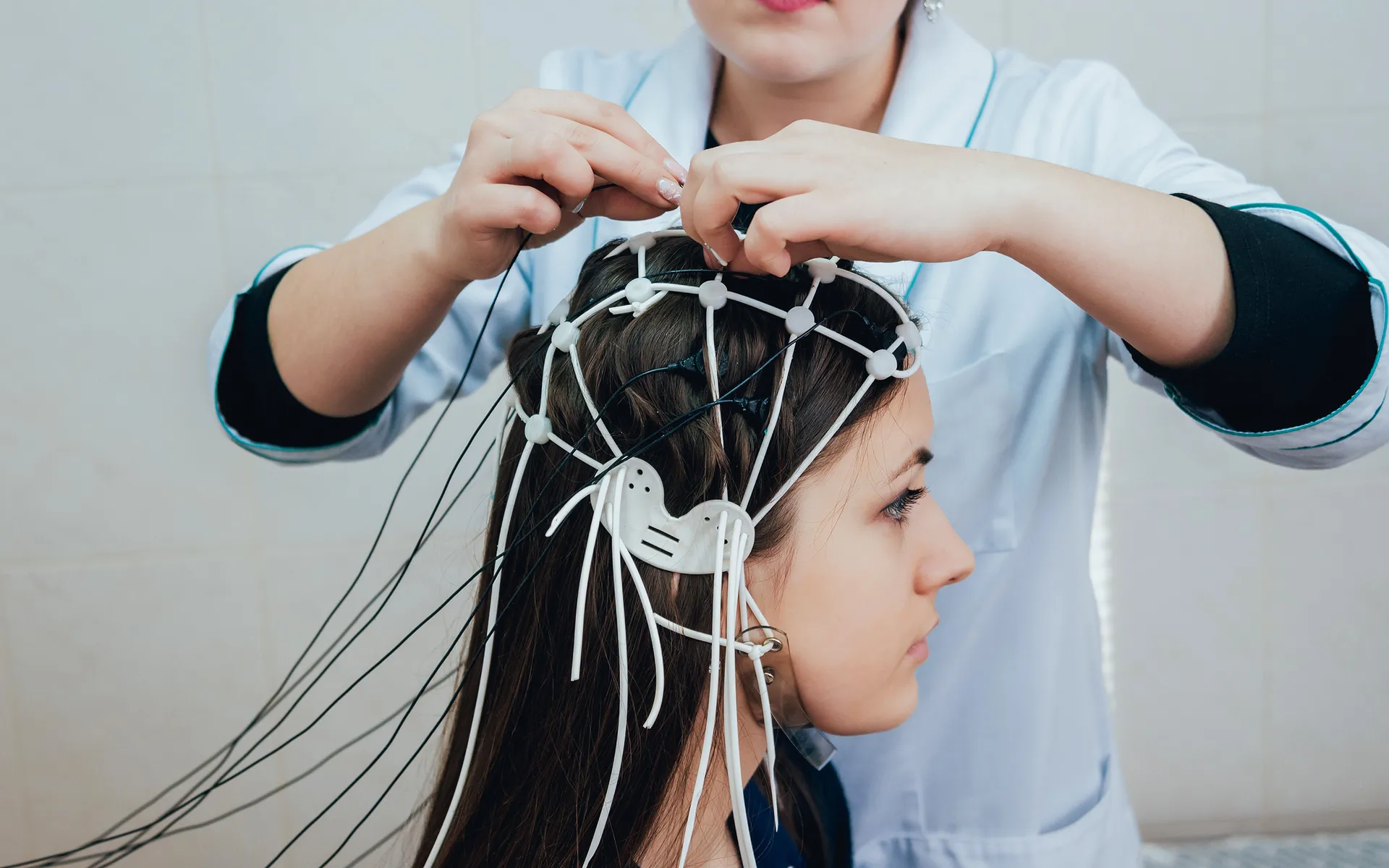

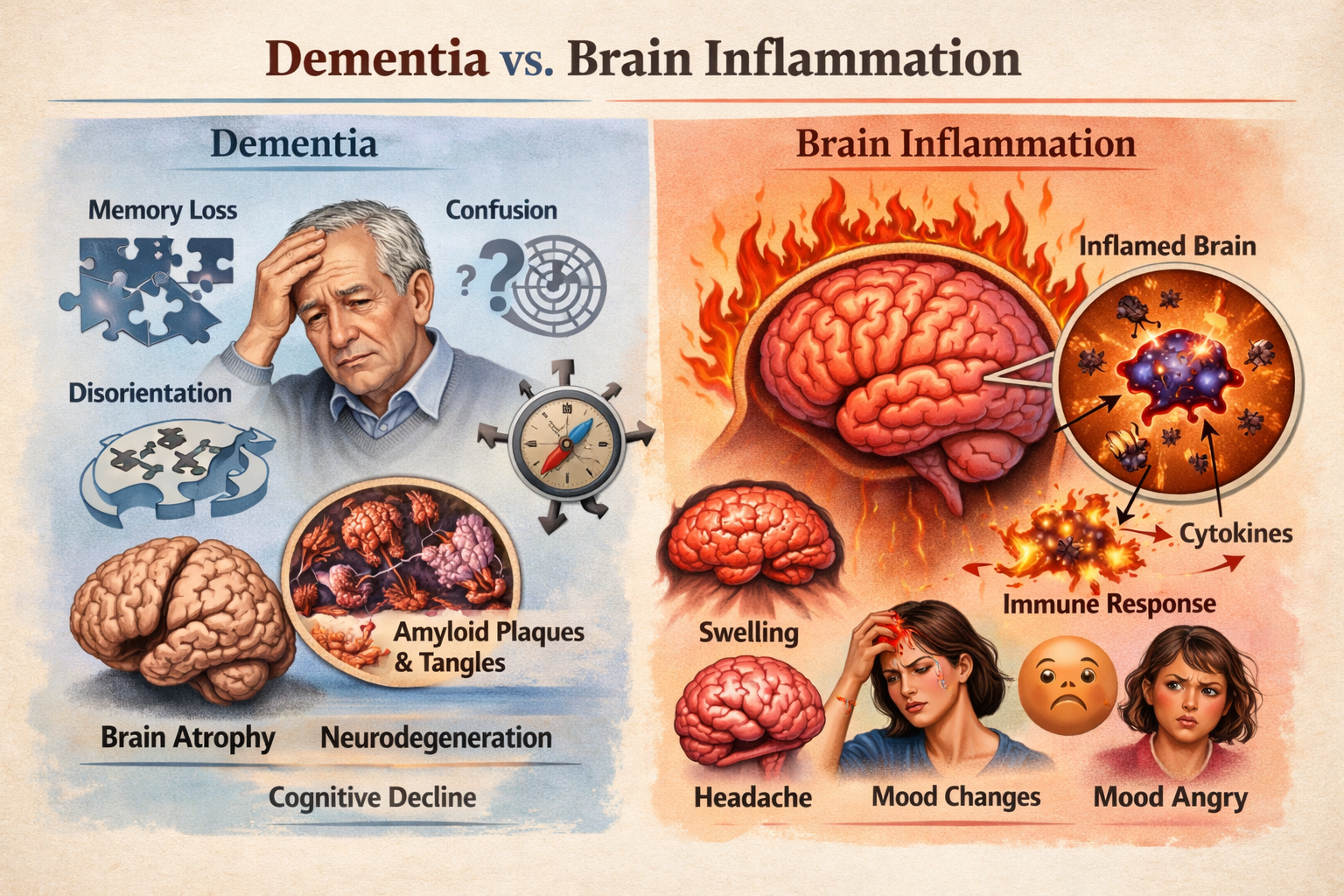
Dementia vs. Brain Inflammation: How to Tell the Difference (And Why It Matters) When someone begins experiencing memory loss, confusion, mood changes, or brain fog , the immediate fear is often dementia. But what many patients and families don’t realize is that brain inflammation can mimic dementia symptoms — and in some cases, it may be reversible. Understanding the difference between dementia and brain inflammation is critical for early intervention, treatment planning, and long-term brain health. What Is Dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term describing a decline in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with daily life. The most common type is Alzheimer's disease, but other forms include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia. Common Dementia Symptoms: Progressive memory loss Disorientation or confusion Difficulty with language Impaired judgment and executive function Personality and behavior changes Gradual decline over time Dementia is typically neurodegenerative , meaning the brain undergoes structural changes such as: Brain atrophy (shrinkage) Amyloid plaque accumulation Tau protein tangles Neuronal loss These changes are generally progressive and irreversible. What Is Brain Inflammation (Neuroinflammation)? Brain inflammation, or neuroinflammation , occurs when the brain’s immune cells become activated in response to stress or injury. Unlike dementia, inflammation can be acute or chronic , and in many cases, potentially treatable. Common Causes of Brain Inflammation: Chronic infections Autoimmune activation Traumatic brain injury (TBI) Mold or environmental toxin exposure Chronic stress Metabolic dysfunction Poor sleep and hormonal imbalance Brain Inflammation Symptoms: Brain fog Short-term memory issues Mood swings or irritability Anxiety or depression Headaches Sensory sensitivity Fatigue Poor concentration Many of these symptoms overlap with early dementia — which is why proper evaluation matters. Can Brain Inflammation Look Like Dementia? Yes. Chronic inflammation can impair: Hippocampal memory circuits Frontal lobe executive function Emotional regulation centers Sleep regulation networks Inflammatory cytokines can alter neurotransmitter balance and reduce metabolic efficiency in brain tissue — leading to cognitive slowdown that resembles early dementia. In clinical practice, identifying inflammation early can dramatically change the treatment path. How to Evaluate Cognitive Decline Properly If you or a loved one is experiencing memory loss or mood changes, a comprehensive evaluation may include: Quantitative EEG (QEEG) brain mapping Cognitive testing Inflammatory lab markers Metabolic and hormonal assessment Sleep analysis Toxic exposure screening Traumatic brain injury history A thorough assessment helps determine whether symptoms reflect neurodegeneration or reversible neuroinflammation . Why Early Identification Matters If the cause is dementia, early intervention can help slow progression. If the cause is inflammation, targeted therapies such as: Neurofeedback Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) Photobiomodulation Nutritional and metabolic support Anti-inflammatory lifestyle strategies may significantly improve cognitive performance and quality of life. Final Thoughts Not all memory problems mean dementia. Sometimes the brain is not failing — it is inflamed. Understanding the difference between dementia and brain inflammation allows patients and families to pursue appropriate testing, targeted treatment, and informed decision-making. If cognitive symptoms are present, early evaluation is critical. Identifying the root cause may open the door to recovery rather than progression.

Contributing Factors of Autism: How Total Toxic Burden Testing Can Help Identify Root Causes Learn about contributing factors of autism, including environmental toxins, heavy metals, and neuroinflammation. Discover how Total Toxic Burden lab testing helps uncover hidden triggers affecting neurodevelopment. Understanding Autism: A Multifactorial Condition Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that does not have a single cause. Current research supports a multifactorial model, meaning autism develops from an interaction between genetic susceptibility and environmental influences—particularly during early brain development. Rather than asking “What caused autism?”, a more productive and scientifically grounded question is: “What factors may be contributing to neurological stress in this individual child?” This is where functional medicine testing, including Total Toxic Burden laboratory analysis, plays a valuable role. Common Contributing Factors of Autism Genetic Vulnerability Certain genetic patterns may affect: Detoxification pathways Methylation and neurotransmitter balance Immune and inflammatory responses Genes alone rarely explain autism—but they can increase sensitivity to environmental stressors. Environmental Toxins and Chemical Exposure One of the most studied contributing factors of autism is early-life toxic exposure. Developing brains are especially vulnerable during pregnancy and the first three years of life. Common exposures include: Heavy metals (mercury, lead, arsenic) Pesticides and herbicides Plastics and endocrine disruptors (BPA, phthalates) Industrial chemicals and solvents Mold toxins (mycotoxins) Even low-level exposure, when combined over time, can place stress on the nervous system. Neuroinflammation and Immune Dysregulation Chronic immune activation may interfere with: Synaptic development Neural connectivity Sensory processing and regulation Toxins, infections, gut dysfunction, and food sensitivities may all contribute to sustained neuroinflammation in susceptible children. Gut–Brain Axis Imbalance The gut plays a critical role in brain development and function. Imbalances in the microbiome can affect: Neurotransmitter production Immune system signaling Detoxification efficiency Gut dysfunction may amplify the neurological impact of environmental toxins. Impaired Detoxification Capacity Some children have difficulty clearing toxins efficiently due to: Genetic detox pathway variants Nutrient deficiencies Chronic inflammation This may result in toxin accumulation, increasing neurological stress even without obvious exposure sources. What Is Total Toxic Burden? Total toxic burden refers to the cumulative amount of environmental toxins present in the body and the physiological strain they place on the brain and nervous system.It’s not about one toxin—it’s about the combined load. For children with autism or developmental delays, this burden may: Disrupt brain signaling Increase irritability and sensory sensitivity Contribute to developmental plateaus or regression Reduce response to therapies if unaddressed How Total Toxic Burden Lab Testing Helps Vibrant Wellness offers a Total Toxic Burden lab test designed to identify hidden toxic contributors that may be impacting neurodevelopment. This comprehensive test assesses: Heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium, arsenic) Environmental chemicals and pesticides Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) Mycotoxins from mold exposure Why this testing matters in autism care: Identifies modifiable environmental contributors Replaces guesswork with objective data Helps personalize nutrition and supplement protocols Guides safe detoxification strategies Supports a root-cause, integrative care model Rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach, this test helps clinicians answer: What is this child’s nervous system responding to right now? From Testing to Targeted Support Once total toxic burden is identified, individualized strategies may include: Environmental exposure reduction (home, food, water) Nutrient repletion to support detox pathways Gut and immune system support Gentle, age-appropriate detox support Integration with neurological therapies such as neurofeedback or developmental rehab This approach is supportive, gradual, and child-centered. A Root-Cause Perspective on Autism Autism is not caused by a single toxin, vaccine, or parenting decision. However, for some children, environmental toxic load may be a significant contributing factor—and one that can be evaluated and addressed. By lowering unnecessary physiological stressors, we help create an internal environment that supports brain regulation, resilience, and developmental progress.Contributing Factors of Autism: How Total Toxic Burden Testing Can Help Identify Root Causes. Learn about contributing factors of autism, including environmental toxins, heavy metals, and neuroinflammation. Discover how Total Toxic Burden lab testing helps uncover hidden triggers affecting neurodevelopment. Understanding Autism: A Multifactorial Condition Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that does not have a single cause. Current research supports a multifactorial model, meaning autism develops from an interaction between genetic susceptibility and environmental influences—particularly during early brain development. Rather than asking “What caused autism?”, a more productive and scientifically grounded question is: “What factors may be contributing to neurological stress in this individual child?” This is where functional medicine testing, including Total Toxic Burden laboratory analysis, plays a valuable role. Common Contributing Factors of Autism Genetic Vulnerability Certain genetic patterns may affect: Detoxification pathways Methylation and neurotransmitter balance Immune and inflammatory responses Genes alone rarely explain autism—but they can increase sensitivity to environmental stressors. Environmental Toxins and Chemical Exposure One of the most studied contributing factors of autism is early-life toxic exposure. Developing brains are especially vulnerable during pregnancy and the first three years of life. Common exposures include: Heavy metals (mercury, lead, arsenic) Pesticides and herbicides Plastics and endocrine disruptors (BPA, phthalates) Industrial chemicals and solvents Mold toxins (mycotoxins) Even low-level exposure, when combined over time, can place stress on the nervous system. Neuroinflammation and Immune Dysregulation Chronic immune activation may interfere with: Synaptic development Neural connectivity Sensory processing and regulation Toxins, infections, gut dysfunction, and food sensitivities may all contribute to sustained neuroinflammation in susceptible children. Gut–Brain Axis Imbalance The gut plays a critical role in brain development and function. Imbalances in the microbiome can affect: Neurotransmitter production Immune system signaling Detoxification efficiency Gut dysfunction may amplify the neurological impact of environmental toxins. Impaired Detoxification Capacity Some children have difficulty clearing toxins efficiently due to: Genetic detox pathway variants Nutrient deficiencies Chronic inflammation This may result in toxin accumulation, increasing neurological stress even without obvious exposure sources. What Is Total Toxic Burden? Total toxic burden refers to the cumulative amount of environmental toxins present in the body and the physiological strain they place on the brain and nervous system. It’s not about one toxin—it’s about the combined load. For children with autism or developmental delays, this burden may: Disrupt brain signaling Increase irritability and sensory sensitivity Contribute to developmental plateaus or regression Reduce response to therapies if unaddressed How Total Toxic Burden Lab Testing Helps Vibrant Wellness offers a Total Toxic Burden lab test designed to identify hidden toxic contributors that may be impacting neurodevelopment. This comprehensive test assesses: Heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium, arsenic) Environmental chemicals and pesticides Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) Mycotoxins from mold exposure Why this testing matters in autism care: Identifies modifiable environmental contributors Replaces guesswork with objective data Helps personalize nutrition and supplement protocols Guides safe detoxification strategies Supports a root-cause, integrative care model Rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach, this test helps clinicians answer: What is this child’s nervous system responding to right now? From Testing to Targeted Support Once total toxic burden is identified, individualized strategies may include: Environmental exposure reduction (home, food, water) Nutrient repletion to support detox pathways Gut and immune system support Gentle, age-appropriate detox support Integration with neurological therapies such as neurofeedback or developmental rehab This approach is supportive, gradual, and child-centered. A Root-Cause Perspective on Autism Autism is not caused by a single toxin, vaccine, or parenting decision. However, for some children, environmental toxic load may be a significant contributing factor—and one that can be evaluated and addressed. By lowering unnecessary physiological stressors, we help create an internal environment that supports brain regulation, resilience, and developmental progress.

Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) and QEEG Brain Mapping: A Data-Driven Approach to Winter Depression Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a form of depression that follows a seasonal pattern, most commonly appearing during the fall and winter months when daylight exposure decreases. While SAD is often dismissed as “winter blues,” research shows it is a neurologically driven condition involving changes in brain activity, circadian rhythms, and neurotransmitter regulation. At Synapse Brain & Spine Center, we use QEEG brain mapping to objectively identify the brain-based patterns associated with SAD and guide personalized treatment strategies such as neurofeedback and integrative neurology care. What Is Seasonal Affective Disorder? Seasonal Affective Disorder is classified as a recurrent depressive disorder with a seasonal onset. Symptoms typically begin in late fall or early winter and improve in spring or early summer. Common Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder Persistent low mood or depression Fatigue and low energy Brain fog and poor concentration Increased sleep or difficulty waking Carbohydrate cravings and weight gain Reduced motivation and productivity Anxiety or emotional reactivity The Brain Science Behind Seasonal Affective Disorder Reduced sunlight exposure affects the brain in several measurable ways: Disrupted circadian rhythm (melatonin and cortisol imbalance) Reduced serotonin signaling, impacting mood regulation Altered frontal lobe activity, affecting motivation and executive function Increased limbic system activation, contributing to anxiety and emotional instability These changes are not subjective—they can be measured using QEEG brain mapping. What Is QEEG Brain Mapping? Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG) is a non-invasive test that measures electrical activity in the brain. It evaluates how different regions communicate and compares results to age-matched normative databases. Unlike MRI or CT scans that look at structure, QEEG assesses brain function. What QEEG Measures: Brainwave speed (delta, theta, alpha, beta, high beta) Regional overactivity or underactivity Functional connectivity between brain regions Patterns associated with depression, anxiety, ADHD, and cognitive fatigue QEEG Patterns Commonly Seen in Seasonal Affective Disorder Patients with SAD often demonstrate consistent findings on QEEG, including: Frontal lobe underactivation Linked to depression, low motivation, and apathy Excess slow-wave activity (theta/alpha) Associated with fatigue, brain fog, and slowed processing speed Frontal–limbic dysregulation Contributes to mood instability and anxiety Left–right hemispheric asymmetries Frequently observed in depressive disorders These findings help explain why many individuals with SAD feel “stuck,” unmotivated, or mentally drained during winter months. Why QEEG Matters for Treating Seasonal Affective Disorder Traditional SAD treatments—such as light therapy or antidepressants—can be helpful, but they often rely on trial and error. QEEG allows treatment to be personalized and data-driven. Benefits of QEEG-Guided Care for SAD: Identifies the root neurological drivers of symptoms Guides QEEG-based neurofeedback protocols Reduces guesswork in treatment planning Objectively tracks progress over time Supports patients who do not tolerate medications well Integrative Treatment Options for SAD at Synapse Brain & Spine Center Using QEEG findings, care plans may include: QEEG-guided neurofeedback to retrain dysregulated brain networks Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) to support cerebral metabolism and neuroplasticity Targeted light and photobiomodulation strategies Circadian rhythm and lifestyle optimizations This integrative approach addresses both brain function and physiological resilience, helping patients feel more stable, energized, and focused throughout the winter. Seasonal Affective Disorder Is Real—and Measurable. Seasonal Affective Disorder is not simply a mood issue or lack of motivation. It is a biologically measurable brain-state change that can be identified and treated with modern functional neurology tools. QEEG brain mapping provides: Objective validation of symptoms Insight into why winter affects your mood and energy A roadmap for personalized, effective treatment If you experience recurring winter depression, fatigue, or cognitive decline, a deeper look at brain function may be the missing piece.

Share On: